Anatomy of a Diamond
Diamonds are precisely cut to enhance brilliance, fire, and scintillation. Each part influences light interaction, affecting beauty and value. Understanding diamond anatomy helps buyers make informed choices.
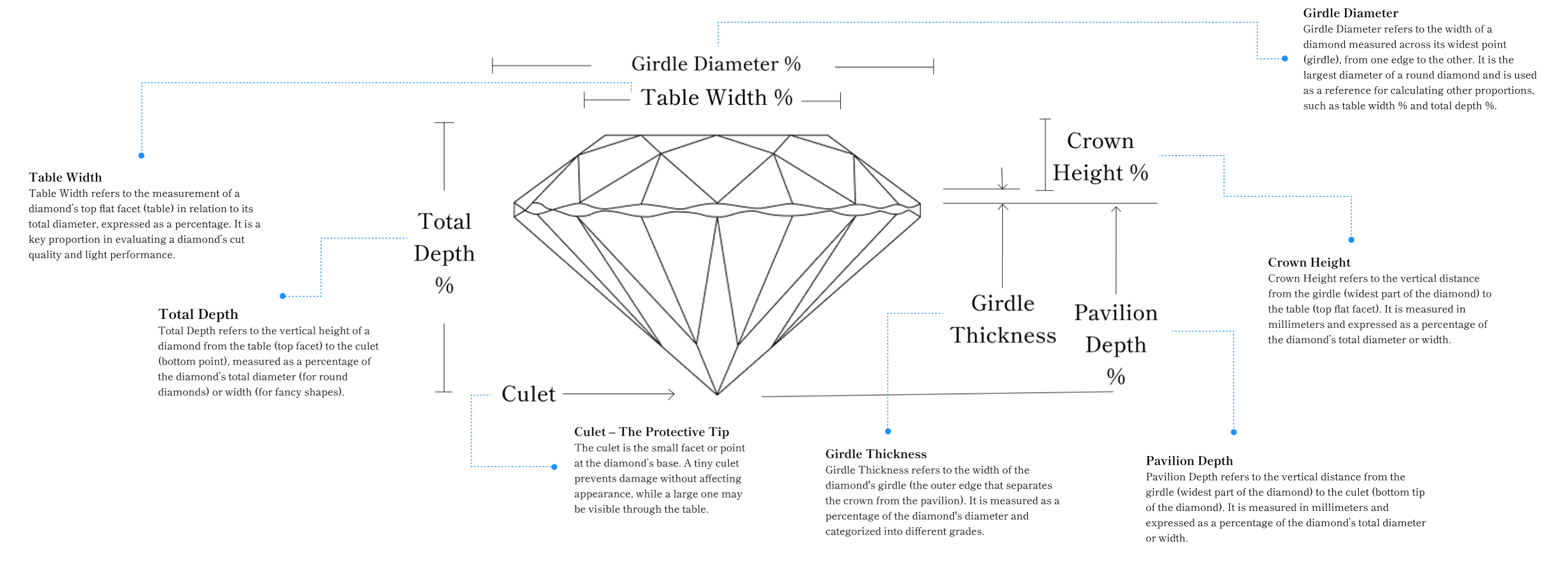
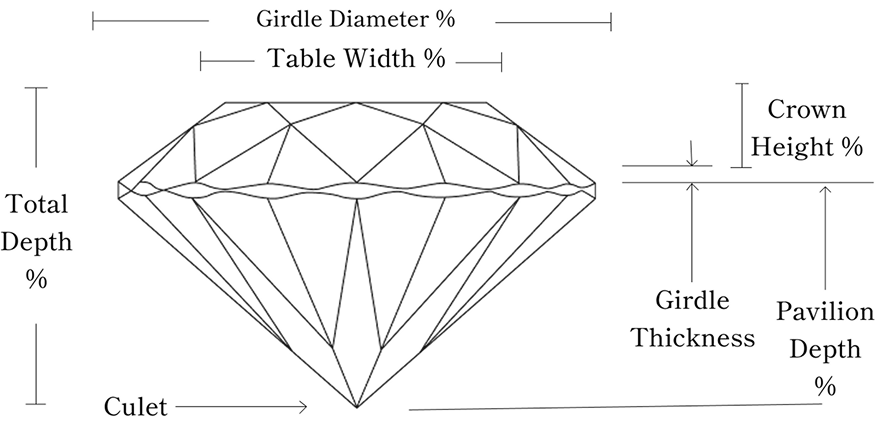
Anatomy of a Diamond
Diamonds are precisely cut to enhance brilliance, fire, and scintillation. Each part influences light interaction, affecting beauty and value. Understanding diamond anatomy helps buyers make informed choices.
Diamond Cut
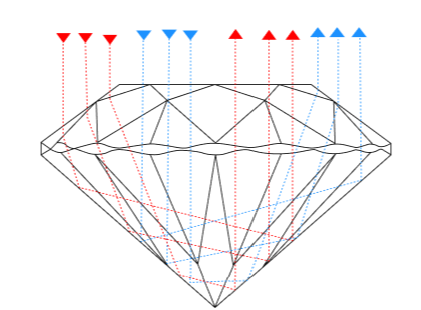
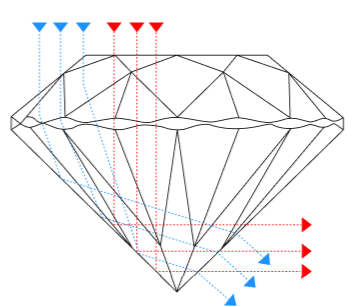
Diamond cut is the most important factor in determining a diamond's brilliance, fire, and overall visual appeal. The GIA (Gemological Institute of America) grades diamond cut based on how well a diamond’s proportions, symmetry, and polish allow light to reflect. Below is an in-depth analysis of each cut grade.
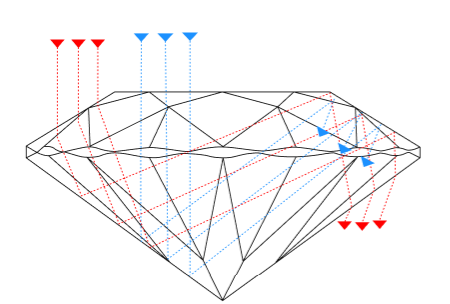
Diamond Color
Diamond color is graded based on how much yellow or brown tint is present in a white diamond. The GIA (Gemological Institute of America) grades diamond color on a scale from D (colorless) to Z (noticeable color).
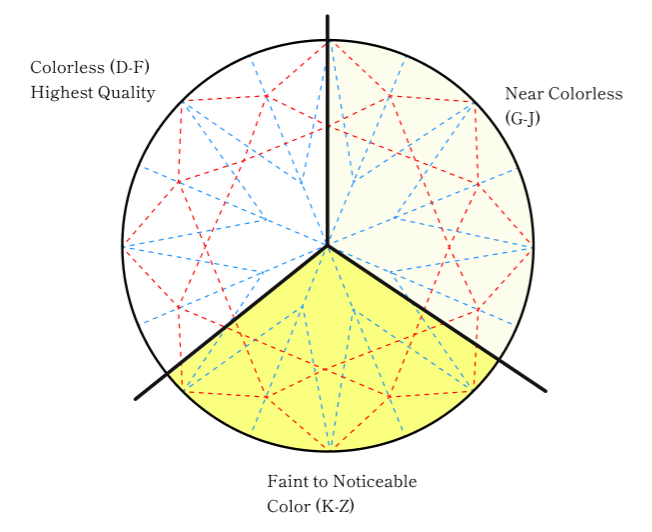
Colorless (D-F) – Highest Quality
- D: Completely colorless, the rarest and most valuable.
- E: Nearly colorless, with only trace amounts of color detectable under magnification.
- F:Slight color presence, but still considered colorless to the naked eye.
Near Colorless (G-J) – Best Value forSparkle
- D: Nearly indistinguishable from colorless unless closely inspected.
- E: Very slight warmth, but still appears white in most settings.
- F: Noticeable tint in larger diamonds, but still a good balance of value.
- j: A faint yellow hue may be visible, especially in larger stones or white gold settings.
K-Z: Warm-Toned Diamonds with Distinctive Appeal
- K-M: Faint yellow hue, still brilliant, pairs beautifully with yellow or rose gold.
- N-R: Light yellow tones, great for creative and antique-inspired designs.
- S-Z: More intense color, offering a bold and vibrant appearance.
Diamond Clarity
Clarity refers to the presence of internal inclusions or external blemishes in a diamond. While most imperfections are microscopic and do not impact beauty, fewer inclusions increase a diamond’s rarity and value.

A Flawless (FL) diamond has no inclusions or blemishes visible under 10x magnification. These diamonds are extremely rare, making them highly valuable.

A Flawless (FL) diamond has no inclusions or blemishes visible under 10x magnification. These diamonds are extremely rare, making them highly valuable.

A Flawless (FL) diamond has no inclusions or blemishes visible under 10x magnification. These diamonds are extremely rare, making them highly valuable.

A Flawless (FL) diamond has no inclusions or blemishes visible under 10x magnification. These diamonds are extremely rare, making them highly valuable.

A Flawless (FL) diamond has no inclusions or blemishes visible under 10x magnification. These diamonds are extremely rare, making them highly valuable.
Diamond Carat
Carat weight measures a diamond’s size, but it’s important to consider how carat interacts with cut, as a well-cut smaller diamond can appear larger than a poorly cut bigger diamond.

Diamond Shapes
Diamond shape refers to the outline and physical form of a diamond when viewed from above. Each shape has distinct characteristics that affect its brilliance, fire, and overall appearance. The right diamond shape depends on personal style, setting preference, and how the shape interacts with light.
Our Commitment

24/7 HOUR HELP

24/7 HOUR HELP

24/7 HOUR HELP

24/7 HOUR HELP

24/7 HOUR HELP









